Sentence Types and Clause Configurations
Diagramming Sentences

COMPOUND
SENTENCE
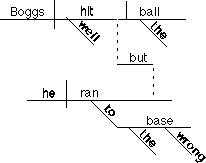
Boggs
hit the ball well, but he ran
to the wrong base.
![]()
Another Example:
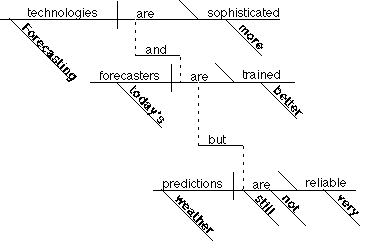
Forecasting technologies are more sophisticated and today's forecasters are better
trained, but weather
predictions are still not very reliable.
![]()
COMPLEX SENTENCES
1.
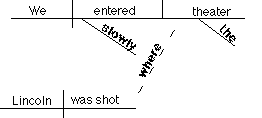
Adjective clause introduced by an adverb
We slowly
entered the theater where Lincoln was shot.
![]()
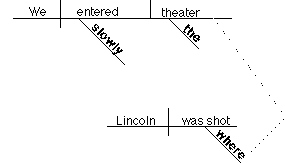
OPTIONAL
METHOD:
We slowly entered the theater
where Lincoln was shot.
![]()
2. Adjective clause introduced by a relative pronoun acting as
subject
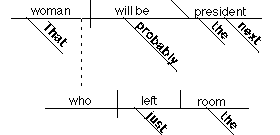
That woman who
just left the room will probably be the next president.
![]()
Another
Example:
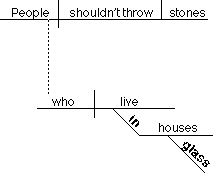
People who live in glass houses shouldn't throw
stones.
![]()
Yet Another Example:
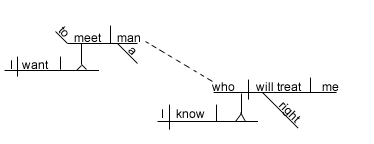
I want
to meet a man who I know will treat me
right.
![]()
3. Adjective
clause introduced by a relative pronoun as direct
object.
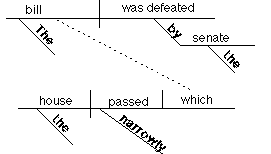
The bill, which
the house narrowly passed, was defeated by the senate.
![]()
Another
Example:
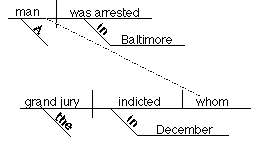
A man whom the grand jury indicted in December was
arrested in Baltimore.
![]()
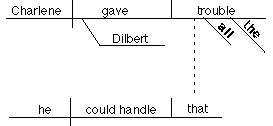
4. Adjective clause modifying a direct object
Charlene gave Dilbert all the trouble that he could handle.
![]()
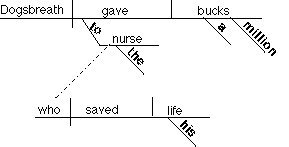
5. Adjective clause modifying the object of a
preposition
Dogsbreath gave a million bucks to
the nurse who saved his
life.
![]()
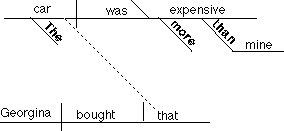
6. Adjective clause modifying the sentence
subject
The car that Georgina bought was more expensive than mine.
![]()
7. Adverb clause modifying the verb
We will
go to the restaurant when
this movie is finished.
![]()
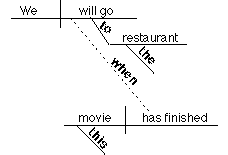
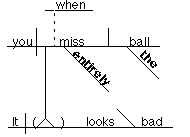
OPTIONAL
METHOD:
It looks bad when you entirely miss the ball. (clause modifies
"looks")
![]()
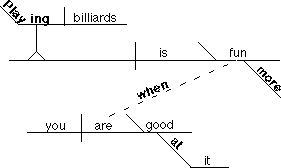
8. Adverb clause modifying an adjective
Playing
billiards is more fun when you are good at it.
![]()
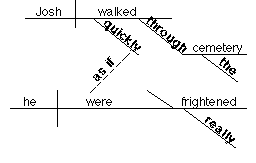
9. Adverb clause modifying an adverb
Josh
walked quickly through the cemetery as if he were really frightened.
![]()
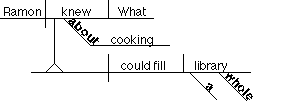
10. Noun clause acting as subject
What Ramon knew about cooking could fill a whole library.
![]()
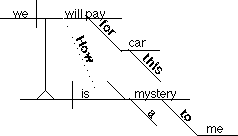
OPTIONAL
METHOD:
How we will
pay for this car is a mystery to me.
![]()
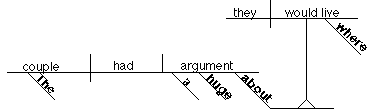
11. Noun clause acting as the the object of a
preposition
The couple had a huge argument
about where they would
live.
![]()
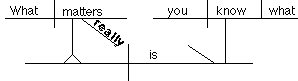
12. Noun clause acting as a predicate noun
What
really matters is what you know.
![]()
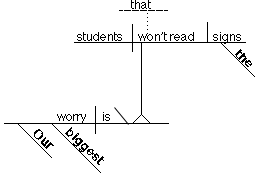
Another
example:
Our biggest worry is
that students won't read the signs.
![]()
13. Noun clause acting as the object of the
sentence
The New Yorker quickly rejected
whatever Sarah submitted.
![]()

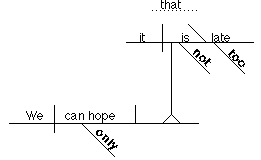
Another
example:
We can only hope [that] it is not too late. (where the word "that" is
omitted)
![]()
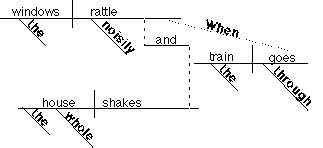
COMPOUND-COMPLEX
SENTENCE
When
the train goes through, the windows rattle
noisily and the whole house shakes.
![]()
 Guide to
Grammar and Writing
Guide to
Grammar and Writing